No mundo atual, onde a competição é acirrada e as expectativas dos consumidores estão sempre evoluindo, é essencial adotar abordagens inovadoras para o desenvolvimento de produtos e serviços.
Uma dessas abordagens é o Design Thinking, uma metodologia centrada no usuário que promove a criatividade, a colaboração e a resolução de problemas de forma eficaz.
Neste artigo, vamos explorar como o Design Thinking pode ser aplicado para impulsionar seu negócio. Conheça as etapas, metodologias e ferramentas essenciais para criar soluções centradas no usuário e alcançar o sucesso no mercado.
O que é Design Thinking?
Design Thinking é uma abordagem para a resolução de problemas complexos e desenvolvimento de soluções inovadoras, centradas no ser humano. Em vez de focar apenas na análise lógica e racional dos problemas, o Design Thinking incorpora a criatividade, a empatia e a experimentação para encontrar soluções eficazes e impactantes.
O conceito de Design Thinking não tem uma origem específica. No entanto, foi a partir das décadas de 1960 e 1970 ele começou a ser utilizado como uma metodologia de resolução de problemas. A empresa de consultoria IDEO, fundada em 1991, desempenhou um papel fundamental na popularização do Design Thinking, promovendo-o como uma abordagem amplamente aplicável para a inovação e o design de produtos, serviços e experiências.
Desde então, o Design Thinking tem sido amplamente adotado por empresas e organizações em todo o mundo como uma ferramenta poderosa para a inovação e a resolução de problemas.
Quais são os pilares do Design Thinking?
O Design Thinking possui pilares muito bem estruturados para auxiliar os profissionais a encontrarem soluções eficazes e inovadoras. Esses elementos formam o alicerce do processo, garantindo que as soluções desenvolvidas estejam verdadeiramente alinhadas com as necessidades e desejos dos usuários.
Empatia com a pessoa usuária
A empatia no Design Thinking vai além da simples compreensão das necessidades dos usuários. Envolve a imersão no contexto dos usuários, buscando entender suas emoções, motivações e comportamentos. Isso pode ser alcançado por meio de entrevistas, observações e até mesmo experiências vividas pelos profissionais.
Foco no problema
Ao estabelecer uma relação de empatia, observação e interação com pessoas usuárias reais, os profissionais conseguem estabelecer o real problema ou identificar uma nova oportunidade de mercado. Assim, o foco é direcionado para as reais necessidades do público/negócio.
Diversidade de ideias
O objetivo de um processo de Design Thinking é gerar o maior número possível de ideias, independentemente de quão absurdas ou improváveis possam parecer. A diversidade de perspectivas é incentivada, e técnicas como brainstorming e mapa de empatia são comumente utilizadas para chegar a solução mais eficiente e disruptiva.
Prototipar a solução
A prototipagem é uma etapa crucial do processo de Design Thinking, permitindo que as equipes transformem suas ideias em um protótipo que pode ser testado e refinado. Os protótipos podem variar de baixa fidelidade (como esboços em papel) a alta fidelidade (como protótipos funcionais).
Teste
Realizar testes frequentes é essencial para promover avaliações rigorosas por parte dos usuários. Isso pode envolver testes de usabilidade, entrevistas, questionários e análise de métricas de desempenho. Os resultados dos testes são utilizados para aprimorar as soluções, garantindo que elas atendam efetivamente às necessidades e expectativas.

Quais são os benefícios do Design Thinking?
O Design Thinking gera diversos benefícios para o seu negócio e para o seu produto digital, essenciais para empresas que desejam se destacar em um mercado cada vez mais competitivo.
Colaboração interdisciplinar
O Design Thinking promove a colaboração entre profissionais de diferentes áreas, como designers, engenheiros, especialistas em marketing e usuários finais. Essa colaboração multidisciplinar proporciona uma variedade de perspectivas e experiências, enriquecendo o processo de design e resultando em soluções mais abrangentes e inovadoras.
Estímulo à criatividade
O Design Thinking incentiva a criatividade ao encorajar os participantes a pensar de forma não convencional e explorar novas abordagens para resolver problemas. As técnicas de brainstorming, prototipagem e visualização ajudam a liberar a criatividade e a gerar ideias inovadoras que podem não surgir em métodos de design mais tradicionais.
Foco nas necessidades reais das pessoas usuárias
Uma das principais premissas do Design Thinking é colocar as necessidades dos usuários no centro do processo de design. Isso garante que as soluções desenvolvidas atendam efetivamente às necessidades reais do público, proporcionando uma experiência mais significativa e satisfatória.
Cria soluções eficazes
Ao adotar uma abordagem centrada no usuário e iterativa, o Design Thinking permite desenvolver soluções mais eficazes e alinhadas com as necessidades do mercado. A prototipagem rápida e os testes frequentes garantem que as soluções sejam refinadas e aprimoradas ao longo do tempo, resultando em produtos e serviços de alta qualidade.
Promove a inovação
O Design Thinking é um catalisador para a inovação, incentivando a exploração de novas ideias, conceitos e tecnologias. Ao desafiar o senso comum e pensar de forma disruptiva, as equipes de design podem desenvolver soluções verdadeiramente inovadoras que se destacam no mercado e proporcionam vantagens competitivas.
Melhoria contínua de produto/serviço
A abordagem iterativa do Design Thinking permite a melhoria contínua de produtos e serviços ao longo do tempo. Os feedbacks dos usuários são constantemente coletados e incorporados ao processo de design, garantindo que as soluções evoluam para atender às necessidades em constante mudança do mercado e do público-alvo.
Aumento na satisfação do cliente
Ao criar produtos e serviços centrados no usuário, o Design Thinking contribui para uma maior satisfação do cliente. Ao entender e atender às necessidades dos usuários de forma eficaz, as empresas podem construir relacionamentos mais fortes e duradouros com seus clientes, aumentando a fidelidade e a retenção.
Adaptação às mudanças do mercado e do público
O Design Thinking capacita as empresas a se adaptarem rapidamente às mudanças do mercado e do público-alvo. A flexibilidade no processo de design permite que as organizações respondam de forma ágil e eficaz às novas tendências, demandas dos consumidores e novos desafios.
Redução de riscos
Ao testar ideias e protótipos rapidamente, o Design Thinking ajuda a mitigar riscos ao longo do processo de desenvolvimento. Identificar e corrigir problemas cedo reduz a probabilidade de falhas e aumenta as chances de sucesso no lançamento do produto ou serviço.
Economia de recursos
O Design Thinking pode resultar em economia de recursos ao longo do ciclo de vida do projeto. Ao priorizar a identificação e resolução de problemas desde o início, as empresas podem evitar retrabalhos e investimentos em soluções que não atendem às necessidades dos usuários.

Quais são as principais metodologias aplicadas no Design Thinking?
No processo de Design Thinking, várias metodologias são utilizadas para compreender melhor as pessoas usuárias, identificar problemas e desenvolver soluções eficazes. Conheça alguns métodos que são mais comuns.
Brainstorming
O brainstorming é uma técnica amplamente utilizada no Design Thinking para gerar ideias criativas e soluções inovadoras. Durante uma sessão de brainstorming, os participantes são encorajados a compartilhar livremente suas ideias, sem críticas ou julgamentos. Isso promove a colaboração e a diversidade de perspectivas, estimulando a geração de soluções inovadoras para os problemas identificados.
Entrevistas com usuários
As entrevistas com usuários são uma parte essencial do processo de Design Thinking, permitindo que os designers entendam melhor as necessidades, desejos e comportamentos dos usuários finais. Durante as entrevistas, os designers fazem perguntas abertas e exploratórias para obter insights valiosos que orientam o desenvolvimento de soluções centradas no usuário.
Criação de personas
As personas são representações fictícias de diferentes tipos de usuários com base em dados reais e insights obtidos por meio de pesquisas e entrevistas. Criar personas ajuda os designers a entenderem melhor quem são seus usuários-alvo, quais são suas necessidades e objetivos, e como podem criar soluções que atendam efetivamente a esses perfis de usuário.
Aprenda mais sobre personas neste material exclusivo.
Mapeamento da jornada do usuário
O mapeamento da jornada do usuário é uma técnica que permite aos designers visualizarem e entenderem a experiência completa do usuário ao interagir com um produto ou serviço. Isso envolve identificar todos os pontos de contato entre o usuário e o produto, desde a descoberta inicial até a conclusão da tarefa, e analisar as emoções, expectativas e desafios enfrentados pelo usuário em cada etapa do processo.
Conheça 7 formas de analisar a jornada do usuário neste artigo do Nielsen Norman Group.
Análise de Dados
A análise de dados é uma prática essencial no Design Thinking, que envolve a coleta, interpretação e aplicação de dados para informar o processo de design. Isso pode incluir dados quantitativos, como métricas de desempenho e comportamento do usuário, e dados qualitativos, como feedback de entrevistas e testes de usabilidade.
A análise de dados ajuda os designers a tomarem decisões informadas e baseadas em evidências ao longo do processo de design.
Teste de Usabilidade
O teste de usabilidade é uma metodologia crucial no Design Thinking, que envolve a avaliação do produto ou serviço em desenvolvimento por parte dos usuários reais.
Essa abordagem ajuda a garantir que o produto ou serviço atenda efetivamente às necessidades e expectativas dos usuários, resultando em uma experiência mais satisfatória e bem-sucedida.
Veja o nosso Guia Completo sobre Teste de Usabilidade.
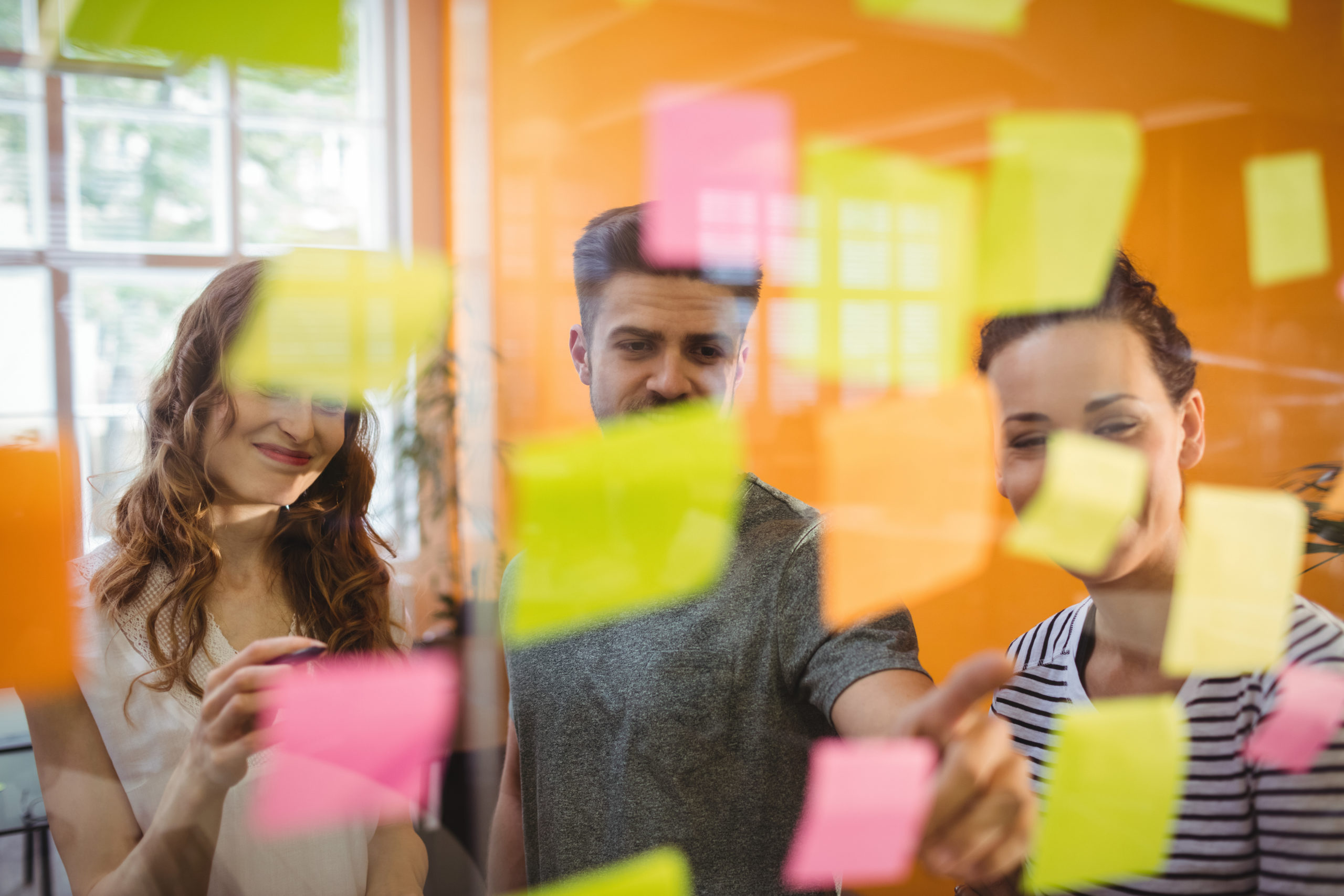

Quais são as etapas do processo de Design Thinking?
Para realizar um projeto utilizando a metodologia do Design Thinking, é essencial concluir alguns passos. Cada etapa é crucial para garantir que a solução final atenda às necessidades e expectativas dos usuários, otimizando recursos.
Compreensão do problema
A primeira etapa do Design Thinking é a compreensão do problema. Aqui, a equipe de design se dedica a entender profundamente o desafio que precisa ser resolvido. Para isso, os profissionais podem realizar pesquisas, entrevistas com stakeholders e análise de dados relevantes.
O objetivo é entender profundamente o problema, seus contextos e os impactos que ele tem nas partes interessadas.
Observação
Na etapa de observação, os designers observam e estudam e imergem no contexto do problema. Eles observam diretamente como as pessoas interagem com o sistema ou o ambiente em questão. Conforme a natureza do negócio/serviço, os profissionais realizam observação de campo, análise de documentos e dados existentes.
Empatia com a pessoa usuária
A empatia com o usuário é uma etapa fundamental do Design Thinking e é desenvolvida por meio de uma profunda compreensão das necessidades, desejos e dores das pessoas envolvidas.
Isso geralmente é alcançado por meio de entrevistas em profundidade, observação direta e empatia ativa, onde os designers se colocam no lugar dos usuários para entender suas perspectivas e experiências.
Definição do problema
Após compreender completamente o problema e as necessidades dos usuários, a equipe de design define claramente o problema a ser resolvido. Isso envolve a formulação de uma declaração de problema concisa e precisa, que orienta o restante do processo de design.
Ideação da solução
Durante a fase de ideação, os designers geram uma ampla variedade de ideias e soluções potenciais para resolver o problema definido. Isso é feito por meio de sessões de brainstorming, workshops colaborativos e outras técnicas de geração de ideias, onde a criatividade é incentivada e as ideias são exploradas livremente.
Prototipagem da solução
Após a geração de ideias, os designers transformam as soluções selecionadas em protótipos tangíveis e testáveis. Isso pode envolver a criação de modelos físicos, wireframes digitais, ou até mesmo simulações interativas. O objetivo é criar representações concretas das soluções propostas que podem ser testadas e refinadas com os usuários.
Teste
Durante a fase de teste, os protótipos desenvolvidos são submetidos a avaliações rigorosas por parte dos usuários reais. Isso pode incluir testes de usabilidade, entrevistas, questionários e análise de métricas de desempenho. Os resultados dos testes são utilizados para aprimorar as soluções, garantindo que elas atendam as expectativas.
Implementação
A implementação é a etapa final do processo de Design Thinking, onde as soluções finalizadas são lançadas no mercado ou integradas aos sistemas existentes da empresa. Isso envolve a coordenação de recursos, a garantia de qualidade e o monitoramento do desempenho das soluções implementadas.
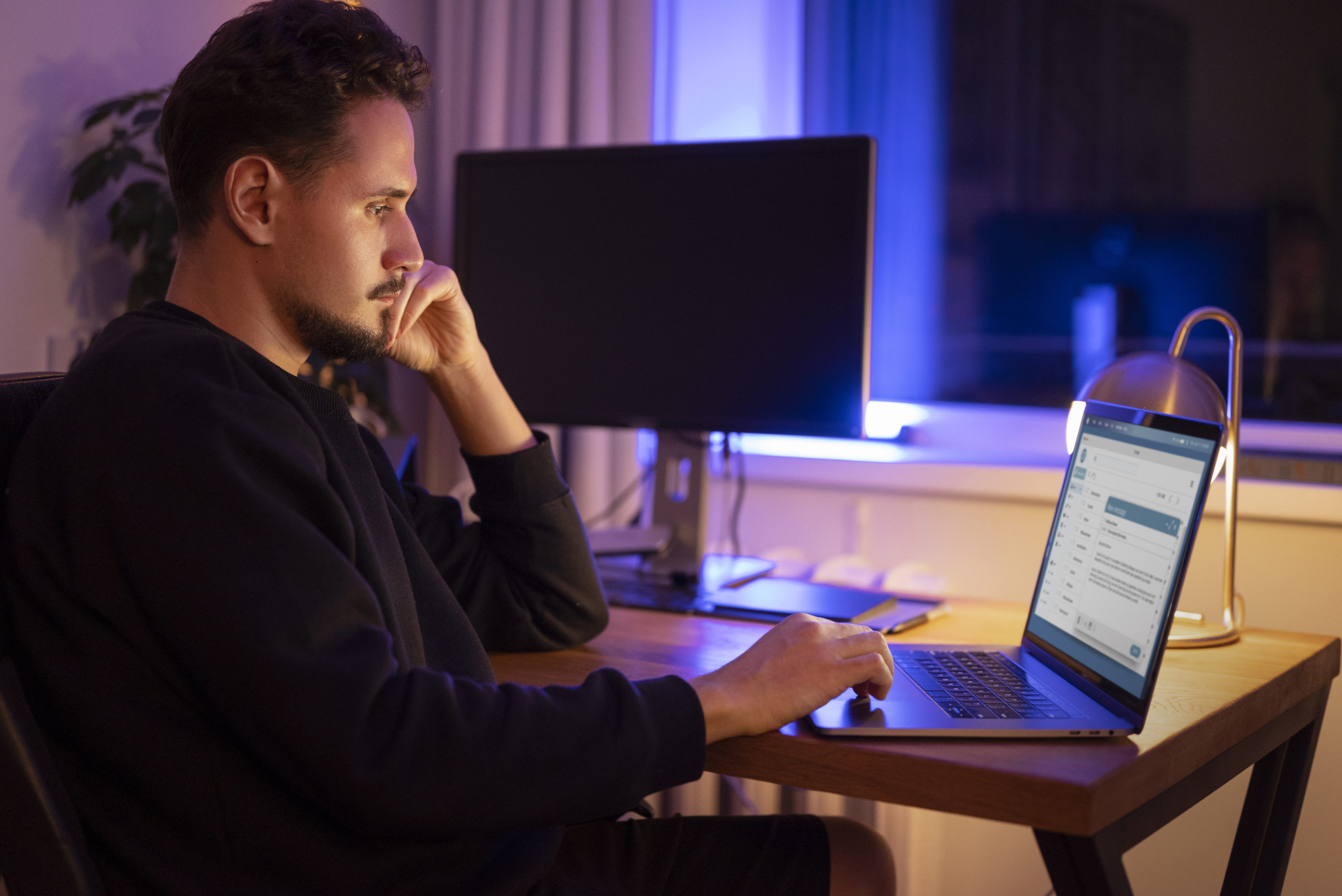

Quais ferramentas podem me auxiliar no processo de Design Thinking?
Na jornada de Design Thinking, contar com as ferramentas certas pode ser a chave para desbloquear a criatividade, promover a colaboração e impulsionar a inovação. Desde a análise inicial até a prototipagem e testes finais, diversas técnicas podem ser potencializadas com o uso de metodologias e plataformas especializadas.
Vamos explorar algumas das ferramentas mais eficazes que podem auxiliar em cada etapa do processo. Fique atento aos links, pois separamos templates prontos para serem utilizados.
Análise SWOT
A análise SWOT é uma técnica essencial para avaliar os pontos fortes, fracos, oportunidades e ameaças de um projeto ou produto. Ferramentas como o Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets ou até mesmo templates online especializados podem ser utilizados para organizar e visualizar os resultados dessa análise de forma clara e concisa.
Aprenda como fazer uma análise SWOT clicando aqui.
Brainstorming
O brainstorming é uma das técnicas mais conhecidas e poderosas do Design Thinking para geração de ideias. Plataformas colaborativas como Miro, Figma ou Jamboard permitem que equipes remotas ou presenciais colaborem em tempo real, compartilhando e organizando ideias de forma visual e dinâmica.
Pesquisa Desk
Para coletar informações e insights valiosos, a pesquisa desk é uma metodologia essencial. Plataformas como Google Acadêmico , Scopus, ACM Digital Library, IEEE Xplore, oferecem acesso a uma vasta gama de artigos acadêmicos, estudos de caso e pesquisas que podem embasar o processo de design com evidências sólidas. Além disso, sempre pode contar com as fontes oficiais de pesquisas, como o IBGE, e as bibliotecas digitais de universidades.
Mapa de Empatia
O mapa de empatia é uma técnica poderosa para entender as necessidades e emoções dos usuários. Ferramentas como Canvas, Adobe XD ou mesmo papel e caneta podem ser usadas para criar mapas de empatia visualmente cativantes, que auxiliam a equipe a se colocar no lugar do usuário.
Aprenda como fazer um Mapa de Empatia no artigo “Empathy Mapping: The First Step in Design Thinking” do Nielsen Norman Group
Prototipagem rápida
Para transformar ideias em realidade de forma rápida e eficiente, a prototipagem rápida é essencial. Ferramentas como Figma, Miro ou InVision permitem que equipes criem protótipos interativos e testáveis em questão de horas, permitindo iterações ágeis e feedbacks imediatos.
Veja como fazer uma prototipagem rápida com este tutorial do Figma.
Cocriação
A cocriação é uma abordagem colaborativa que envolve usuários no processo de design desde o início. Ferramentas como Zoom, Microsoft Teams ou Slack permitem que equipes e stakeholders se conectem virtualmente para workshops e sessões de cocriação, garantindo que todas as vozes sejam ouvidas. Você pode usar o Figma ou Miro para reunir as ideias e debater a melhor abordagem.
Aprenda mais sobre o que é um workshop de cocriação e como aplicar.
Jornada do Usuário
Para mapear e compreender a experiência do usuário ao longo do tempo, a jornada do usuário é uma ferramenta valiosa. Plataformas como Lucidchart, UXPressia, Figma, Miro ou até mesmo templates de PowerPoint podem ser usados para criar jornadas do usuário visualmente envolventes, que destacam pontos de dor e oportunidades de melhoria.
Aprenda mais sobre jornada do usuário neste artigo.
Teste de Usabilidade
Por fim, o teste de usabilidade é fundamental para validar e aprimorar as soluções propostas. Ferramentas como Hotjar, Optimal Workshop, User Testing ou Lookback permitem que equipes conduzam testes de usabilidade remotos ou presenciais, capturando feedbacks valiosos que informam iterações futuras.

Qual é a relação entre Design Thinking e UX?
O Design Thinking e o UX Design são abordagens que possuem um objetivo em comum: proporcionar experiências significativas e satisfatórias para os usuários.
Enquanto o Design Thinking é um processo estratégico para resolver problemas de forma criativa, o UX Design foca na experiência do usuário ao interagir com um produto ou serviço.
A sinergia entre essas metodologias resulta em soluções centradas no usuário que são funcionais, intuitivas e envolventes. Técnicas complementares, ao serem aplicadas em conjunto, oferecem diversos benefícios para os negócios.
Compreensão profunda do usuário
Ambas as abordagens enfatizam entender os usuários. O Design Thinking busca essa compreensão por meio de empatia e observação, enquanto o UX Design se concentra na pesquisa de usuários e análise de comportamento.
Foco na experiência
Ambas as metodologias colocam a experiência do usuário no centro do processo de design, visando criar soluções que atendam às suas necessidades e expectativas.
Melhoria contínua
O Design Thinking e o UX Design adotam uma abordagem iterativa, permitindo que as soluções sejam constantemente testadas e melhoradas com base no feedback dos usuários.
Impacto nos resultados de negócios
Ao integrar Design Thinking e UX Design, as organizações podem criar produtos e serviços que impulsionam o sucesso nos negócios, impactando a satisfação do cliente e a reputação da marca.
Quais são os benefícios do Design Thinking para criação/evolução de um produto digital?
O Design Thinking oferece uma série de vantagens para a criação e evolução de produtos digitais, garantindo uma abordagem abrangente e orientada para o usuário na a criação e evolução de produtos digitais, contribuindo para o sucesso e a competitividade desses produtos no mercado.
Para a criação ou evolução de um produto digital, o Design Thinking oferece uma série de benefícios, incluindo identificação de oportunidades e inovação, melhoria na experiência do usuário, aumento na eficácia do produto digital e redução dos custos de desenvolvimento. Esses benefícios são essenciais para empresas que buscam se destacar em um mercado em constante evolução.
Como vimos anteriormente, o Design Thinking garante que os produtos digitais sejam intuitivos, acessíveis e agradáveis de usar. Ao entender profundamente as necessidades e desejos dos usuários, os designers podem criar interfaces e funcionalidades que ofereçam uma experiência de usuário excepcional.
Além disso, produtos digitais concebidos com base no Design Thinking destacam-se devido à sua ênfase na inovação, usabilidade e satisfação do usuário. Essa abordagem cria um diferencial competitivo significativo, tornando os produtos mais atraentes para os usuários e aumentando suas chances de sucesso.
Aprenda mais sobre User Experience
Acompanhe outros posts sobre User Experience em nosso blog:
Descubra como as personas melhoram a experiência do usuário
Guia completo sobre Teste de Usabilidade
Tudo o que você precisa saber sobre UX Design
Nós da Tuia
Aqui na Tuia oferecemos soluções para empresas que buscam melhorias para seus produtos através do design e conteúdo.
Se interessou por nosso método de trabalho? Entre em contato conosco.
Nos acompanhe também em nossas páginas no LinkedIn e no Instagram.